ASTER MISSION
GENERAL INFORMATION
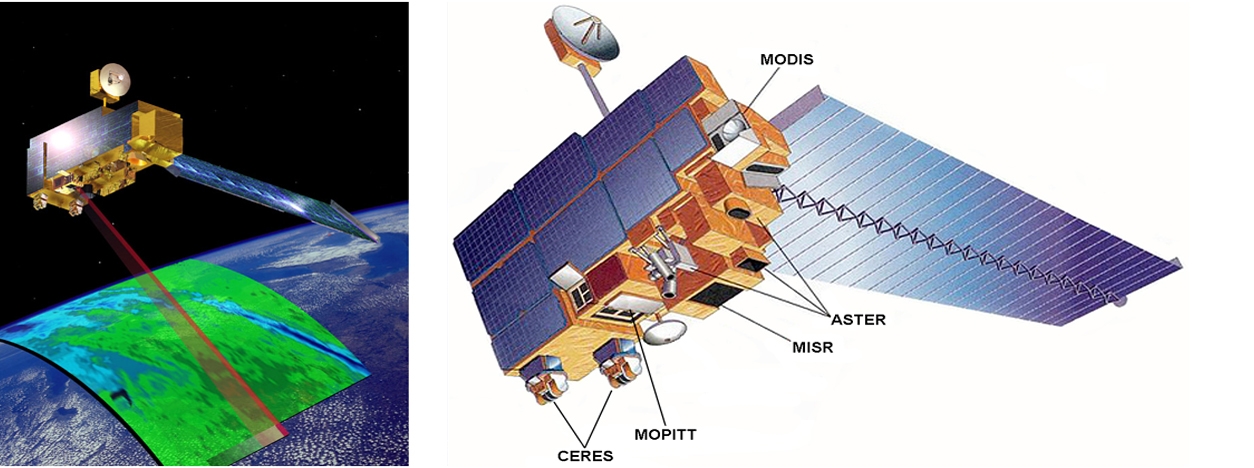
The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument is a remote sensing device developed by the Japanese government in cooperation with NASA. It was launched onboard the Terra satellite in 1999 and has been collecting data since February 2000. ASTER captures high-resolution images of the Earth’s surface in 14 different bands of the electromagnetic spectrum, from visible to thermal infrared light.
The ASTER mission is a collaboration between NASA and Japan’s Ministry of Economy Trade and Industry (METI), as well as scientific and industry organizations in both countries. The instrument offers improved remote sensing capabilities compared to older sensors such as the Landsat Thematic Mapper and Japan’s JERS-1 OPS scanner. ASTER data is used for validation and calibration by other instruments onboard the Terra satellite and other space-borne platforms.
ASTER images have a resolution ranging between 15 and 90 meters, with a temporal resolution of 16 days. The data has been used for various applications, including land cover and land use classification, urban expansion assessment, forest and crop monitoring, water resource management, natural disaster response and recovery, and climate change studies.
ASTER data is freely available to the public through various portals such as NASA’s Earth Data Search delivery system or the USGS Earth Explorer delivery system.
ASTER Missions
The ASTER instrument was launched onboard the Terra satellite in 1999. It is made up of a set of sensors, including the Visible and Near Infrared Radiometer (VNIR), Short-Wave Infrared Radiometer (SWIR), and Thermal Infrared Radiometer (TIR).
In 2009, a comprehensive mapping of the Earth’s surface known as the Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM) was released to the public. The GDEM covers 99% of the Earth’s land area and was created using stereo-correlation to create individual scene-based ASTER DEM.
ASTER sensor is made of a set of sensors:
- VNIR (Visible and Near Infrared Radiometer)
- SWIR (Short-Wave Infrared Radiometer)
- TIR (Thermal Infrared Radiometer)
| Mission | Launch Year | Sensor |
| ASTER | 1999 | VNIR, SWIR, TIR |
| ASTER Global DEM | 2009 | VNIR, SWIR, TIR |
TECHNICAL DETAILS
The ASTER instrument captures images with a spatial resolution of 15 meters for the panchromatic band and between 30 meters and 90 meters for other bands. The radiometric resolution of the data is 8 bits for VNIR and SWIR bands and 12 bits for TIR bands. The instrument has a temporal resolution of around 16 days, meaning each location on Earth is imaged about once every 16 days, weather permitting.
ASTER can acquire stereo images, which can be used to generate digital elevation models (DEMs) of the Earth’s surface. The instrument has a swath width of 60 kilometers and a repeat cycle of 16 days.
| ASTER Mission | Primary Sensor | Bands | Spatial Resolution | Radiometric Resolution | Spectral Range | Temporal Resolution |
| Terra | ASTER | 5 | VNIR: 15 meters; SWIR: 30 meters; TIR: 90 meters | VNIR and SWIR: 8-bit, TIR: 12-bit | VNIR: 0.52-0.86 µm; SWIR: 1.6-2.43 µm; TIR: 8.125-11.65 µm | 16 days |
| ASTER Global DEM | ASTER | 3 | 30 meters | 8-bit | VNIR: 0.52-0.86 µm; SWIR: 1.6-2.43 µm | N/A |
The ASTER instrument has 14 spectral bands with a spatial resolution ranging between 15 and 90 meters.
The bands are named:
| Band | Name | Wavelength (µm) |
| 1 | Visible | 0.52-0.60 |
| 2 | Visible | 0.63-0.69 |
| 3N | Near Infrared | 0.78-0.86 |
| 3B | Near Infrared | 0.78-0.86 |
| 4 | Shortwave Infrared | 1.60-1.70 |
| 5 | Shortwave Infrared | 2.145-2.185 |
| 6 | Shortwave Infrared | 2.185-2.225 |
| 7 | Shortwave Infrared | 2.235-2.285 |
| 8 | Shortwave Infrared | 2.295-2.365 |
| 9 | Shortwave Infrared | 2.360-2.430 |
| 10 | Thermal Infrared | 8.125-8.475 |
| 11 | Thermal Infrared | 8.475-8.825 |
| 12 | Thermal Infrared | 8.925-9.275 |
| 13 | Thermal Infrared | 10.25-10.95 |
| 14 | Thermal Infrared | 10.95-11.65 |
MAIN APPLICATIONS AND DATA ACCESS
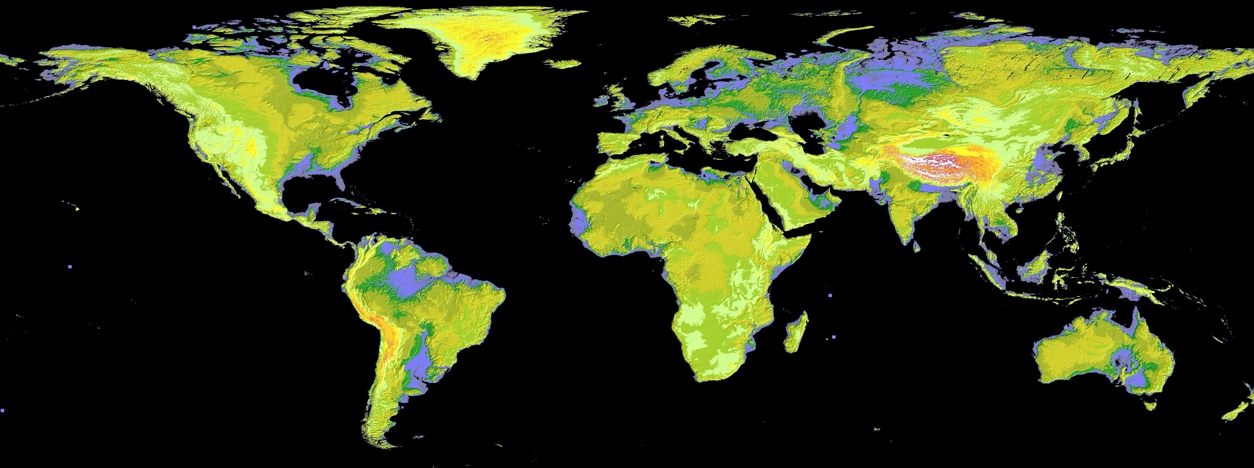
The high-resolution nature of ASTER data makes it valuable for various applications, including:
- Land cover and land use classification
- Urban expansion assessment
- Forest and crop monitoring
- Water resource management
- Natural disaster response and recovery
- Climate change studies
- Digital Elevation Models (DEM)
ASTER data is publicly available for free through various portals such as NASA’s Earth Data Search delivery system or the USGS Earth Explorer delivery system. Data can be downloaded in several different digital formats and processed using a variety of software packages.
RELATED LINKS AND ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
Further background information about ASTER:
- ASTER Mission – This is the official website for the ASTER mission, which provides information on the science behind ASTER.
Accessing and working with ASTER data:
- NASA Earth Data Search – This is the main site for searching and downloading ASTER data. It allows users to search for and download data by location, date range, and other criteria.
- NASA Earth Data Search – This portal allows users to search for and download data by location, date range, and other criteria.
- USGS Earth Explorer – This portal also provides access to ASTER data, as well as other remote sensing data products.
- Google Earth Engine – Google Earth Engine is a cloud-based platform for working with geospatial data, including ASTER data. It provides access to pre-processed ASTER data and a range of analysis tools.
- Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology
- ASTER Land Surface Temperature
*Images from
https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/nasa-japan-release-most-complete-topographic-map-of-earth
https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/learn/articles/terra-at-20
https://www.nasa.gov/directorates/heo/scan/images/history/December1999.html

