Land Use Land Cover
GENERAL INFORMATION
Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) is a fundamental concept in geography, environmental science, urban planning, and various other fields. It involves studying and categorizing how land is used and its physical attributes. LULC data is essential for understanding the Earth’s surface and its changes over time.
LULC comprises two key components:
- Land Use:Refers to the human activities conducted on the land, such as agriculture, residential development, industrial areas, and recreational spaces.
- Land Cover:Describes the physical characteristics of the land, encompassing natural elements like forests, water bodies, wetlands, barren land, and urban infrastructure.
LULC is categorized and studied through a variety of classification schemes and systems. It provides insights into how humans interact with the environment and is used for diverse purposes.
Key areas where LULC analysis is essential include:
- Urban Planning:Understanding urban expansion and infrastructure development.
- Environmental Management:Assessing the impact of land use changes on ecosystems.
- Resource Management:Allocating resources effectively based on land use patterns.
In LULC analysis, researchers often employ classification schemes like the Anderson Land Use Classification System. These systems standardize the categorization of land into distinct types based on predefined criteria. Such schemes facilitate the organization and interpretation of LULC data.
For the study of LULC, quantifying the changes over time is fundamental. Techniques for detecting and monitoring land use and cover changes include:
- Image Differencing:This technique directly compares two or more LULC maps over the same area, taken at different times, by subtracting pixel values or using other methods.
- Time Series Analysis:Time series analysis is a more comprehensive approach that involves using multiple images taken over a period, often at regular intervals.
- Machine Learning Algorithms:Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) have become increasingly crucial in LULC analysis. These algorithms can automate detecting and classifying changes in land use and cover. They can work with large datasets, recognize patterns that may not be obvious to the human eye, and improve accuracy.
MAIN SOURCES OF LULC
LULC analysis relies on data from various sources, including remote sensing, Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and ground surveys. Satellite imagery, aerial photography, and ground-based data collection methods contribute to comprehensive LULC assessments. Satellite sensors provide invaluable data for LULC mapping. They offer spatial and temporal coverage, allowing large-scale monitoring and analysis of land cover changes. High-resolution satellite imagery is particularly useful for detailed LULC studies.
- Remote Sensing:Satellite and aerial imagery provide valuable large-scale land cover analysis data. Remote sensing is fundamental for collecting and classifying LULC based on automatic or semi-automatic approaches.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS):GIS technology aids in the collecting (on-screen photo interpretation), processing, analysis, and visualization of LULC data.
- Ground Surveys:Field surveys and data collection provide ground-truth information to validate remote sensing results.
LULC FOR EUROPE – CLC Project
The main (official) LULC database for Europe is derived from the Corine Land Cover Project. The Corine Land Cover (CLC) is a pan-European initiative to provide detailed and consistent land cover information for the entire European continent. It is managed by the European Environment Agency (EEA) in collaboration with European countries. The project’s primary objective is to create and update land cover and land use databases, providing valuable insights into land cover changes over time and supporting environmental policy development, monitoring, and reporting at regional, national, and European levels.
Years Available:
- CLC1990: The initial release covering land cover information from 1990.
- CLC2000: The second edition with data from the year 2000.
- CLC2006: An update that provides information for 2006.
- CLC2012: The 2012 dataset offering the most recent land cover information.
- CLC2018: The latest update, providing land cover data for 2018.
Key Technical Details:
- Spatial Resolution:The spatial resolution of CLC data is 100 meters, meaning each pixel in the dataset represents a 100-meter by 100-meter area on the ground.
- Number of Land Cover Classes:CLC classifies land cover into a comprehensive set of land cover and land use classes. The number of classes may vary slightly between editions, but it typically includes around 40 primary classes and a more detailed subclassification, resulting in over 100 land cover classes.
- Data Sources:CLC data is generated primarily by interpreting satellite imagery, aerial photography, and other Earth observation data sources. It involves combining automated classification techniques and manual on-screen digitalization to ensure accuracy.
- Data Format:CLC data is typically available in vector format (e.g., shapefiles) and raster format (e.g., GeoTIF), making it compatible with various GIS software.
- Accuracy and Validation:The CLC project strongly emphasizes data accuracy and undergoes rigorous validation processes to ensure the quality of the information provided.
- Data Access:CLC data is freely accessible to the public and can be obtained from the official European Environment Agency (EEA) website, where users can download datasets for specific years and regions of interest.
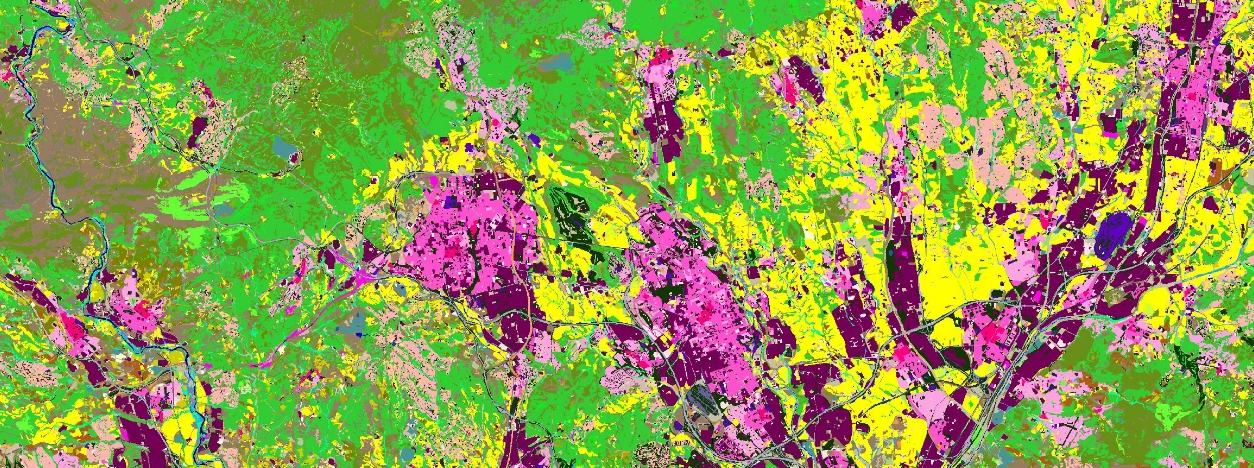
LULC FOR MILAN
The DUSAF dataset – Uso e Copertura del Suolo – offers valuable insights into the land use and cover patterns for the Lombardy region. It is a detailed geographic database initiated in 2000/2001 and has since reached its 7th version (DUSAF 7.0). In this latest version, orthophotos with a ground resolution of 0.2 meters per pixel were utilized, taken in 2021. The entire regional territory has been updated regarding land use, land cover, hedges, and rows up to 2021. The level of detail corresponds to an informative scale of 1:10,000, which means:
- For representing area-based elements:
- For each thematic element with an area of representation, the minimum dimensional threshold corresponds to 1600 square meters, which equates to a cartographic area at a 1:10,000 scale of 16 square millimeters.
- The minimum linear size of a polygon is 20 meters, equivalent to a length on the map at the working scale of 2 millimeters.
- For representing linear elements (rows and hedges):
- They are represented if their linear development on the ground is greater than 40 meters (within individual plots of land they cover).
- Rows and hedges are surveyed when their width exceeds 5 meters.
Regarding geometric modifications of existing polygons, all deviations greater than 20 meters from the existing arc have been considered, regardless of the modified area’s size (which may be smaller than the minimum cartographic area). DUSAF 7.0 is also published in “Temporal Evolution DUSAF” for comparison with previous versions for 1999, 2007, 2009, 2012, 2015, and 2018.
The DUSAF legend is structured into 5 hierarchical levels, with the first 3 consisting of classes from the Corine Land Cover project. The first level includes 5 general classes covering major land cover types (Urban Areas, Agricultural Areas, Forested Areas, Semi-natural Environments, Wetlands, and Water Bodies), further differentiated in the subsequent 2 levels. The need to represent certain local specificities led to introducing two additional levels (4 and 5), which, when present, describe distinctive elements of the Lombardy region’s territory. These peculiarities were mainly derived from supplementary databases available to complete the work.
LULC FOR BARCELONA
The CREAF | Ecological and Forestry Applications Research Centre provides high-resolution cartographic information on land cover types in Catalonia, such as urban areas, agricultural lands, forests, and water bodies.
- Spatial Resolution: 1 meter.
- Thematic Resolution: 41 classes.
- Data Date: 2009 and 2018.
The Land Covers of 2009 are primarily a simplification into 41 classes of the Land Cover Map of Catalonia v4 from 2009 prepared by CREAF, along with an adaptation to the data model approved by the Cartographic Coordination Commission of Catalonia, enabling comparison between that geoinformation and the subsequent one.
The Land Covers of 2018is an update of the Land Covers 2009, carried out based on the photointerpretation of the ICGC 2018 orthophotos. Changes more significant than 2 hectares were identified by comparing LANDSAT images from the two years. Changes from the ICGC 1:5,000 topographic database and data from forest fire records and SIGPAC were considered in this update. The layer of changes between 2012 and 2018 from Corine Land Cover was also considered, with particular attention to the categories “Conreus en Transformació” (Transforming Crops) and “Zones en Transformació” (Transforming Zones) from the 2009 version due to their significant dynamics.
Exceptionally, due to the large volume of changes in agricultural areas in Lleida and the coastal area from Tarragona to Barcelona, only agricultural changes more significant than 5 hectares were photo-interpreted. Supervision was carried out on a sample of 811 points across the entire territory, resulting in a thematic quality, or level of agreement between independent labeling and the labeling, by the team that conducted the significant changes update from 2009 to 2018, of 81%. The raster format of the Land Covers is used solely as a data structure to store transformed data from the vector format Land Covers through interpolation processes.
MAIN APPLICATIONS OF LAND USE LAND COVER

Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) analysis is a cornerstone in geography, environmental science, and urban planning, offering invaluable insights into the intricate relationship between human activities and the natural environment. Beyond its role as a scientific endeavor, LULC analysis finds profound applications that resonate across various domains, delivering both practical and strategic advantages.
And Use Land Cover Analysis
LULC analysis is vital for many compelling reasons, each underlining its unique ability to deliver valuable insights and support informed decision-making.
- LULC is crucial for assessing the consequences of human activities on ecosystems and biodiversity. Understanding how landscapes transform over time equips us to evaluate the impact on flora and fauna, land degradation, and habitat fragmentation.
- In urban planning, LULC data is indispensable. It provides essential insights for sustainable growth, aiding resource allocation and infrastructure planning, ensuring cities develop purposefully and strategically.
- Prudent resource allocation relies on understanding land use patterns. LULC analysis supports interpreting these patterns, enabling informed decision-making for optimizing agriculture, protecting water resources, and ensuring sustainable forestry management.
- Climate change, one of the most pressing global challenges, is intricately linked to land use and land cover dynamics. LULC analysis plays a pivotal role in monitoring and mitigating climate change. It tracks carbon sequestration, the depletion of forests, and other factors contributing to this critical issue. By understanding how our land use practices impact the planet, we can take meaningful steps towards climate resilience.
Real-World Applications
The versatility of LULC analysis translates into real-world applications that resonate across various domains:
Urban Growth Studies:LULC data is used to monitor the expansion of urban areas, enabling cities to plan for infrastructure and services.
Deforestation Monitoring:It aids in tracking deforestation rates, assessing the loss of biodiversity, and mitigating climate change.
Habitat Conservation:LULC analysis helps identify and conserve critical habitats for wildlife.
Land Management:LULC analysis informs sustainable land management practices, facilitating responsible land use and resource allocation.
Climate Change Impact Assessment:LULC data is crucial for evaluating how climate change affects land cover and ecosystems.
RELATED LINKS AND ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
Further background information about LULC
- Land Use Codes – The Official Web Site for The State of New Jersey– This webpage provides detailed information about land use codes in New Jersey. It explains the Anderson Classification System used for land use/land cover data layers.
- Land Use/Land Cover | Earthdata– This is NASA’s Earthdata website, which provides information on the observed physical cover and natural use of the land, including the vegetation and human construction that covers the earth’s surface.
- NASA SVS | Global MODIS Land Cover– This webpage provides a detailed picture of the distribution of Earth’s ecosystems and land use. It helps scientists better determine how vegetation is distributed and how land is used worldwide.
- Global Land Cover Datasets – NASA– This page offers access to a number of datasets which describe land cover characteristics at 1°×1° resolution.
- ESA global land cover map– This is ESA’s global land cover map, which is ten times sharper than any previous global satellite map. It is now available to the public online from the GlobCover website.
- ESA CCI Land cover website– This website provides information about the activities and key achievements of the CCI Land Cover team over the last years.
Accessing and working with LULC
- CORINE Land Cover– The CORINE Land Cover website provides information on the CORINE Land Cover project in Europe. It includes sections on the project’s history, methodology, and data access.
- National Land Cover Database | U.S. Geological Survey (usgs.gov) – This is the National Land Cover Database website, which provides information on the NLCD project in the United States. It includes sections on the project’s history, methodology, and data access.
- ESA WorldCover – This is the ESA WorldCover website, which provides information on the ESA WorldCover project. It includes sections on the project’s methodology, data access, and applications.
- Geoportale della Lombardia – This is the official Geoportal of Lombardia. It allows users to search for geographic data in the Catalog of Regione Lombardia, access maps, download data, and use WMS and WFS services.
- Cobertes del sòl. Institut Cartogràfic i Geològic de Catalunya – This webpage provides high-resolution cartographic information about the land cover types in Catalonia, such as urbanized areas, agricultural areas, forests, bodies of water, etc. It also provides download links for the images.
*Images from
https://www.esa.int/About_Us/ESRIN/Express_map_delivery_from_space

